Next: Single and Multi Step
Up: Minimal Spanning Trees
Previous: Distances
Contents
Mean Occupation Layer
Changes in the density, or spread, of the MST can be examined through calculation of the mean occupation layer, as defined by Onnela et al. [20]:
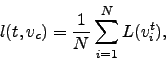 |
(2.29) |
where 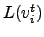 denotes the level of a node, or vertex,
denotes the level of a node, or vertex, 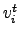 in relation to the central node, whose level is defined as zero. The central node can be defined as the node with the highest number of links or as the node with the highest sum of correlations of its links. Both criteria produce similar results. The mean occupation layer can then be calculated using either a fixed central node for all windows, or with a continuously updated node.
in relation to the central node, whose level is defined as zero. The central node can be defined as the node with the highest number of links or as the node with the highest sum of correlations of its links. Both criteria produce similar results. The mean occupation layer can then be calculated using either a fixed central node for all windows, or with a continuously updated node.
Ricardo Coelho
2007-05-08